Explore the severe legal outcomes that follow a hit-and-run accident, highlighting why it’s never a wise choice to flee the scene.

Understanding Hit-and-Run Accidents: Definitions and Examples
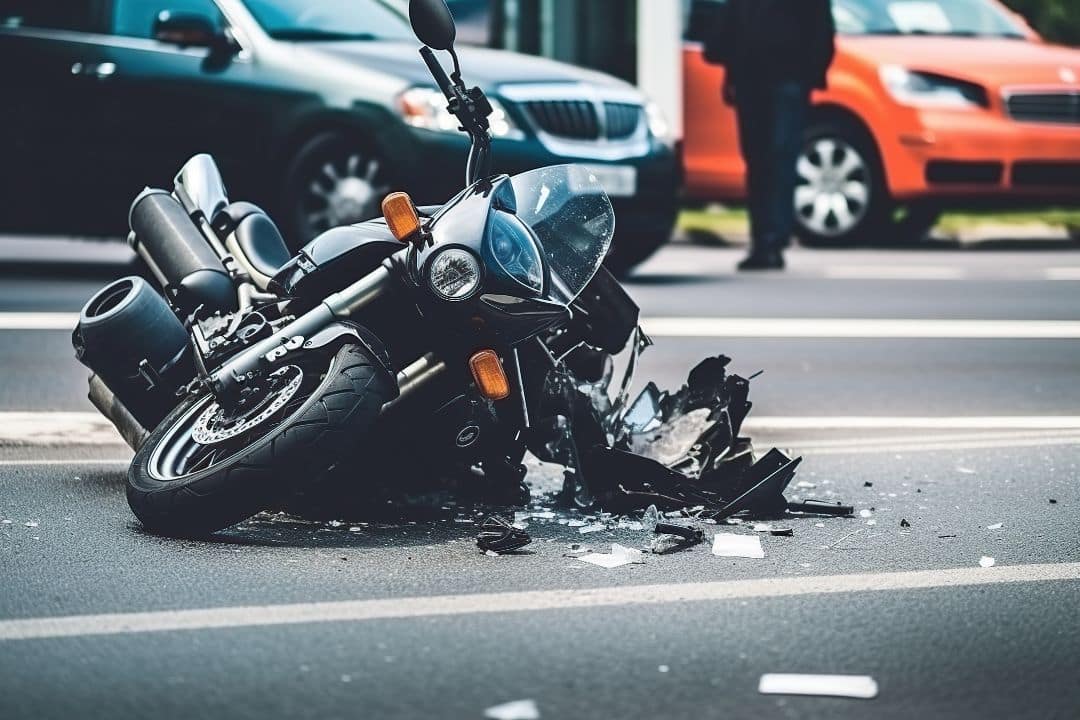
Hit-and-run accidents occur when a driver involved in a vehicular collision leaves the scene without providing contact information or rendering aid to the other party. These incidents can range from minor fender benders to severe crashes resulting in injury or death. Examples of hit-and-run scenarios include a driver striking a parked car without leaving a note, colliding with a pedestrian and not stopping, or rear-ending another vehicle and speeding away without exchanging insurance details.
Understanding the definition and examples of hit-and-run accidents is crucial in recognizing the serious nature of these offenses and the corresponding legal implications. In these cases, the driver who flees fails to fulfill their legal and moral obligations, often exacerbating the consequences for all involved parties.
State-by-State Variations in Hit-and-Run Laws
The legal consequences of hit-and-run accidents are not uniform across the United States; they vary significantly from state to state. Some states classify these incidents as misdemeanors with penalties including fines and jail time, while others consider more serious hit-and-runs as felonies, potentially leading to years of imprisonment. Factors that influence the severity of the punishment include the extent of property damage, bodily injuries, or fatalities resulting from the accident.
Drivers must be aware of the specific hit-and-run laws and penalties within their state. A lack of knowledge does not excuse the responsibility to stay at the scene, and ignorance can lead to harsher legal repercussions.
Criminal Charges and Penalties for Fleeing the Scene
Criminal charges for hit-and-run drivers can be severe, reflecting the gravity of abandoning the scene of an accident. Penalties often include fines, license suspension, and imprisonment. In cases where the hit-and-run resulted in significant injury or death, sentences are harsher, and charges may escalate to felony status. Such convictions can also influence future employment opportunities, insurance rates, and social stigma.
The legal system imposes these penalties to deter drivers from leaving accident scenes and to promote accountability. It’s essential for drivers to understand that the immediate consequences of stopping and facing the situation are almost always less severe than those arising from fleeing.
Civil Liabilities: Compensation and Lawsuits
Apart from criminal consequences, hit-and-run drivers also face civil liabilities. Victims may file lawsuits seeking compensation for medical expenses, lost wages, pain and suffering, and property damage. When a driver is identified after leaving the scene, the court may impose punitive damages as a punishment for the egregious act of fleeing, which can significantly increase the financial burden on the perpetrator.
These civil suits serve to help victims recover from their losses and send a message that negligent behavior resulting in additional trauma for the victim will not be tolerated under the law.
Preventive Measures and How to Respond if Involved in a Hit-and-Run
Preventing hit-and-run accidents begins with education and awareness. Drivers should understand the ethical and legal requirements to remain at the scene, no matter how minor the accident may seem. It’s also vital to know how to respond if involved in a hit-and-run, whether as a perpetrator or a victim. Perpetrators should find a safe place to stop nearby, check for injuries, call emergency services, and wait for authorities to arrive.
Victims should try to note the fleeing vehicle’s description, license plate, and direction of flight, and immediately contact law enforcement. Witnesses can also play a crucial role by providing statements and evidence. The collective effort of the community in deterring hit-and-runs is paramount in ensuring that the roads are safer for everyone.